alsa框架基础
·
ALSA,全称Advanced Linux Sound Architecture(高级Linux音频体系结构),是Linux操作系统上用于管理音频和音频设备的软件架构,为Linux操作系统提供音频和MIDI功能。它提供了一个标准的接口,用于应用程序与硬件之间的音频通信,以及音频设备之间的通信。
ALSA架构主要有两方面组成:
1、Linux内核空间的ALSA驱动,在Linux内核2.6之后,ALSA驱动代码已经集成到Linux源码中。
2、Linux用户空间的ALSA库和程序:alsa-lib、alsa-utils、alsa-tools、alsa-firmware、alsa-plugins、alsa-oss。
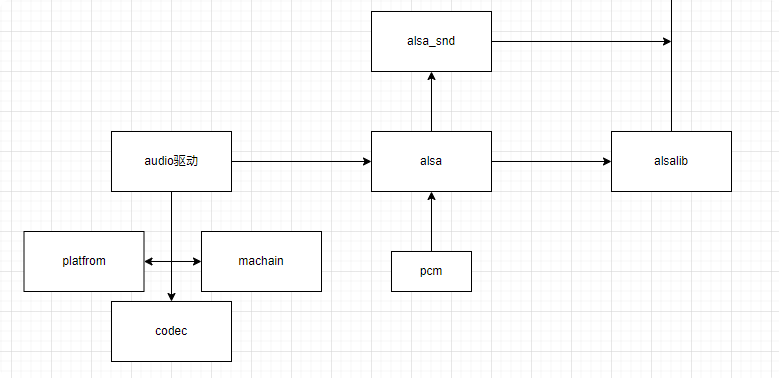
声卡驱动注册后,音频设备控制节点:
/dev/snd/midiC0D0 -->用于播放midi音频
/dev/snd/pcmC0D0c -->用于录音的pcm设备
/dev/snd/pcmC0D0p -->用于播放的pcm设备
/dev/snd/seq -->音序器
/dev/snd/timer -->定时器
alsa将底层硬件驱动分成三部分:machine,platfrom和codec。
machine driver:
用于实现platform和codec的耦合,注册声卡。
platform driver:
dma的注册和管理,用于在内存和codec之间传输数据。
codec driver:
codec_dai的注册和管理,用于实现和driver的耦合,设置采样率,位深的设置。
alsa_lib 用户态提供的api给应用程序使用,即可以完成对底层音频硬件的控制:
int snd_pcm_open(snd_pcm_t **pcm, const char *name, snd_pcm_stream_t stream, int mode); //打开声卡
int snd_pcm_open_lconf(snd_pcm_t **pcm, const char *name, snd_pcm_stream_t stream, int mode, snd_config_t *lconf);
int snd_pcm_open_fallback(snd_pcm_t **pcm, snd_config_t *root, const char *name, const char *orig_name,snd_pcm_stream_t stream, int mode);
int snd_pcm_close(snd_pcm_t *pcm); //关闭声卡
const char *snd_pcm_name(snd_pcm_t *pcm);
snd_pcm_type_t snd_pcm_type(snd_pcm_t *pcm);
snd_pcm_stream_t snd_pcm_stream(snd_pcm_t *pcm);
int snd_pcm_poll_descriptors_count(snd_pcm_t *pcm);
int snd_pcm_poll_descriptors(snd_pcm_t *pcm, struct pollfd *pfds, unsigned int space);
int snd_pcm_poll_descriptors_revents(snd_pcm_t *pcm, struct pollfd *pfds, unsigned int nfds, unsigned short *revents);
int snd_pcm_nonblock(snd_pcm_t *pcm, int nonblock);
static __inline__ int snd_pcm_abort(snd_pcm_t *pcm) { return snd_pcm_nonblock(pcm, 2); }
int snd_async_add_pcm_handler(snd_async_handler_t **handler, snd_pcm_t *pcm, snd_async_callback_t callback, void *private_data);
snd_pcm_t *snd_async_handler_get_pcm(snd_async_handler_t *handler);
int snd_pcm_info(snd_pcm_t *pcm, snd_pcm_info_t *info);
int snd_pcm_hw_params_current(snd_pcm_t *pcm, snd_pcm_hw_params_t *params);
int snd_pcm_hw_params(snd_pcm_t *pcm, snd_pcm_hw_params_t *params); //设置声卡参数
int snd_pcm_hw_free(snd_pcm_t *pcm);
int snd_pcm_sw_params_current(snd_pcm_t *pcm, snd_pcm_sw_params_t *params);
int snd_pcm_sw_params(snd_pcm_t *pcm, snd_pcm_sw_params_t *params);
int snd_pcm_prepare(snd_pcm_t *pcm);
int snd_pcm_reset(snd_pcm_t *pcm);
int snd_pcm_status(snd_pcm_t *pcm, snd_pcm_status_t *status);
int snd_pcm_start(snd_pcm_t *pcm); //启动声卡
int snd_pcm_drop(snd_pcm_t *pcm);
int snd_pcm_drain(snd_pcm_t *pcm);
int snd_pcm_pause(snd_pcm_t *pcm, int enable);
snd_pcm_state_t snd_pcm_state(snd_pcm_t *pcm);
int snd_pcm_hwsync(snd_pcm_t *pcm);
int snd_pcm_delay(snd_pcm_t *pcm, snd_pcm_sframes_t *delayp);
int snd_pcm_resume(snd_pcm_t *pcm);
int snd_pcm_htimestamp(snd_pcm_t *pcm, snd_pcm_uframes_t *avail, snd_htimestamp_t *tstamp);
snd_pcm_sframes_t snd_pcm_avail(snd_pcm_t *pcm);
snd_pcm_sframes_t snd_pcm_avail_update(snd_pcm_t *pcm);
int snd_pcm_avail_delay(snd_pcm_t *pcm, snd_pcm_sframes_t *availp, snd_pcm_sframes_t *delayp);
snd_pcm_sframes_t snd_pcm_rewindable(snd_pcm_t *pcm);
snd_pcm_sframes_t snd_pcm_rewind(snd_pcm_t *pcm, snd_pcm_uframes_t frames);
snd_pcm_sframes_t snd_pcm_forwardable(snd_pcm_t *pcm);
snd_pcm_sframes_t snd_pcm_forward(snd_pcm_t *pcm, snd_pcm_uframes_t frames);
snd_pcm_sframes_t snd_pcm_writei(snd_pcm_t *pcm, const void *buffer, snd_pcm_uframes_t size);
snd_pcm_sframes_t snd_pcm_readi(snd_pcm_t *pcm, void *buffer, snd_pcm_uframes_t size);
snd_pcm_sframes_t snd_pcm_writen(snd_pcm_t *pcm, void **bufs, snd_pcm_uframes_t size);
snd_pcm_sframes_t snd_pcm_readn(snd_pcm_t *pcm, void **bufs, snd_pcm_uframes_t size);
int snd_pcm_wait(snd_pcm_t *pcm, int timeout);
int snd_pcm_link(snd_pcm_t *pcm1, snd_pcm_t *pcm2);
int snd_pcm_unlink(snd_pcm_t *pcm);
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献16条内容
已为社区贡献16条内容







所有评论(0)